1. Introduction
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors reduce blood glucose level in patients with type 2 diabetes by inhibiting degradation of two main incretin hormones. It increases the level of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells [1]. Incretin hormones show inhibition of glucagon release and decrease gastric emptying in addition to insulin secretion. GIP is known to promote the bone formation and GLP-1 is known to inhibit bone absorption [1]. Pleiotropic effects of DPP-4 inhibitors have been reported on various tissues and cell types [2]. The effect on bone metabolism is not fully understood. The paradox of Type 2 diabetes on bone quality is reported as increased fracture risk [3]. A recent meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials of DPP-4 inhibitors showed the reduced risk of bone fractures [4]. Vildagliptin study showed no changes in markers of bone resorption or calcium homeostasis [5]. The exact mechanisms by which DPP-4 inhibitors affect bone quality remain unclear. Glorie et al showed that DPP IV inhibitor treatment attenuated bone loss and improved mechanical bone strength in rats possibly interacting with bone metabolism [6, 7].
Gemigliptin (LG Life Sciences, Ltd., Seoul, South Korea), a recently developed DPP-4 inhibitor, has an excellent glucose-lowering effect [8]. It is known that oxidative stress inhibits osteoblast differentiation [9] and induces apoptosis under high sugar condition [10]. Since antioxidant property of gemigliptin is reported throughout the drug development process, we hypothesized that gemigliptin might induce bone remodeling and protect bone cells from oxidative stress. In this study, we investigated the effects of reducing sugar and gemigliptin treatment on MC3T3-E1 cells in vitro. 2-Deoxy-D-ribose (dRib) is known as the strongest reducing sugar [11]. Because glucose is the least reactive of the reducing sugars [12], we selected dRib to induce oxidative damage in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Here, we investigated the effects of gemigliptin on osteoblastic differentiation and bone quality with and without the presence of dRib.
2. Materials and Methods
MC3T3-E1 murine osteoblastic cells were from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA). The cell culture was conducted in α-modified minimal essential medium (α-MEM; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. The cultures were maintained at 37˚C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere and cultivated using 0.05% trypsin/0.02% EDTA in Ca2+- and Mg2+-free Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline (DPBS) until they reached approximately 70% confluence. For assessment of cell viability, apoptosis and ROS production, the cells were plated in 24-well culture plates at a density of 2 × 104/well. Two days after culture, the cells were treated with gemigliptin for 24 h in α-MEM containing 0.5% FBS. In treatments involving dRib, dRib was added after 1 h of gemigliptin treatment. The cell culture medium was changed every 2 days. After 6 days, the cells were cultured in medium containing dRib and/or gemigliptin for 2 days, and the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, collagen content and gene expression of bone-related markers were then measured.
Cell viability was determined by measuring cell metabolic activity using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (Dojindo Co., Kumamoto, Japan). CCK-8 contains 2-(2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl) -3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, monosodium salt, which produces a water-soluble formazan dye upon reduction in the presence of an electron carrier. The amount of yellow formazan dye generated by the activity of dehydrogenases in cells is directly proportional to the number of living cells. MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells were plated in 24-well cell culture plates at a density of 2 × 104/well. At the end of the culture period, 50 μL CCK-8 solution were added to 500 μL medium in each well of the culture plate. After a 4 h incubation, absorbance was measured using the Zenyth 3100 multimode detector (Anthos Labtec Instruments GmbH, Wals/Salzburg, Austria) at 450 nm using a 650 nm filter as a reference. The viability of cells incubated with culture medium alone was set at 100% and included as the control in all experiments for estimation of the cell viability percentage.
The Cell Death Detection ELISA Kit (Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Mannheim, Germany), which is used for quantitative detection of cytosolic histone-associated DNA fragments, was used to measure apoptosis according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 104/well in 24-well culture plates. The culture conditions were the same as those described for the cell viability assay. Following incubation, the cells were lysed, and intact nuclei were pelleted by centrifugation. An aliquot of the supernatant was used as the antigen source for sandwich ELISA, which was performed using a primary anti-histone monoclonal antibody bound to the streptavidin-coated wells of a microtiter plate. Subsequently, the cells were treated with a second anti-DNA monoclonal antibody coupled to peroxidase. Nucleosome levels were quantified by determining the amount of peroxidase retained in the immunocomplex. Peroxidase activity was determined photometrically at 405 nm using 2,2’-azino-di(3-ethylbenzthiazolin-sulfonate) as the substrate.
The fluorescent probe chloromethyl-2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFDA; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) was used to measure intracellular ROS levels as described previously [13]. MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells were cultured for 24 h in α-MEM containing 0.5% FBS, rinsed twice with DPBS and then treated with 10 μM DCFDA for 1 h. The cells were then rinsed and scraped, and their fluorescence was measured (excitation 485 nm, emission 515 nm) using the Zenyth 3100 multimode detector.
At the time of cell harvesting, the medium was removed and the cell monolayer gently washed twice with PBS. The cells were then lysed with 0.2% Triton X-100, and the lysate was centrifuged at 14,000 g for 5 min. The cleared supernatant was used to measure ALP activity and the protein concentration. ALP activity was determined using an ALP activity assay kit (Somang Engineering Co., Seoul, Korea) and normalized to the number of cells.
Cellular collagen content was measured using the Sircol Collagen Assay Kit (Biocolor Ltd., Newtownabbey, Northern Ireland). This assay is a quantitative dye-binding method designed for the analysis of collagen extracted from mammalian tissues and cells during in vitro culture. The dye reagent binds specifically to the [Gly-X-Y]n helical structure found in mammalian collagen (types I–V). Measurements were normalized to the number of cells.
Total RNA was isolated from cells using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). Following isolation, RNA integrity was assessed using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). cDNA was synthesized using the Transcriptor First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and stored at –70˚C until further processing. All procedures were carried out according to the manufacturers’ protocols.
Real-time PCR was performed to verify the differential expression of select genes by the TaqMan method using the Roche Universal Probe Library (UPL) kit with the Roche LightCycler 480 system (Roche Diagnostics GmbH). Relative gene expression was determined by employing the comparative CT method. All reactions were carried out in a total volume of 20 μL of the reaction mixture containing 10.0 μL 2X UPL master mix, 1.0 μL 5’ primer (10 pmol/μL), 1.0 μL 3’ primer (10 pmol/ μL), 0.2 μL UPL probe, 1.0 μL cDNA and 6.8 μL sterile water. The thermal cycling conditions for PCR were an initial denaturation step for 10 min at 95˚C, followed by 40 cycles of 94˚C for 10 s and 60˚C for 30 s. The primers were designed using the Roche ProbeFinder assay tool. For RT-PCR analysis, duplicate reactions were performed for each cDNA. Negative controls (except templates) were included in the PCR reaction to ensure specific amplification. LightCycler 480 software version 1.2 (Roche Diagnostics GmbH) was used for quantitative PCR analysis. The values obtained from each sample were normalized to hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase expression. The expression levels of each gene in each experimental group were compared with the respective expression levels in the control group. We evaluated ALP, collagen, osteocalcin, osteoprotegerin, osteopontin (OPN), bone sialoprotein, osterix and bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) as bone-related markers. We measured superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) as oxidative stress-related markers. We also measured the osteoblast-related signal transduction markers phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K), AKTs and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs).
3. Results
We evaluated cell viability using the CCK-8 assay to assess the effect of dRib on MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cell survival. Dose-dependent decrease in cell viability was observed in the cells exposed for 24 h to various concentrations of dRib (Fig. 1A). At 30 mM dRib, we observed approximately 50% inhibition of cell viability by 24 h under our experimental conditions.
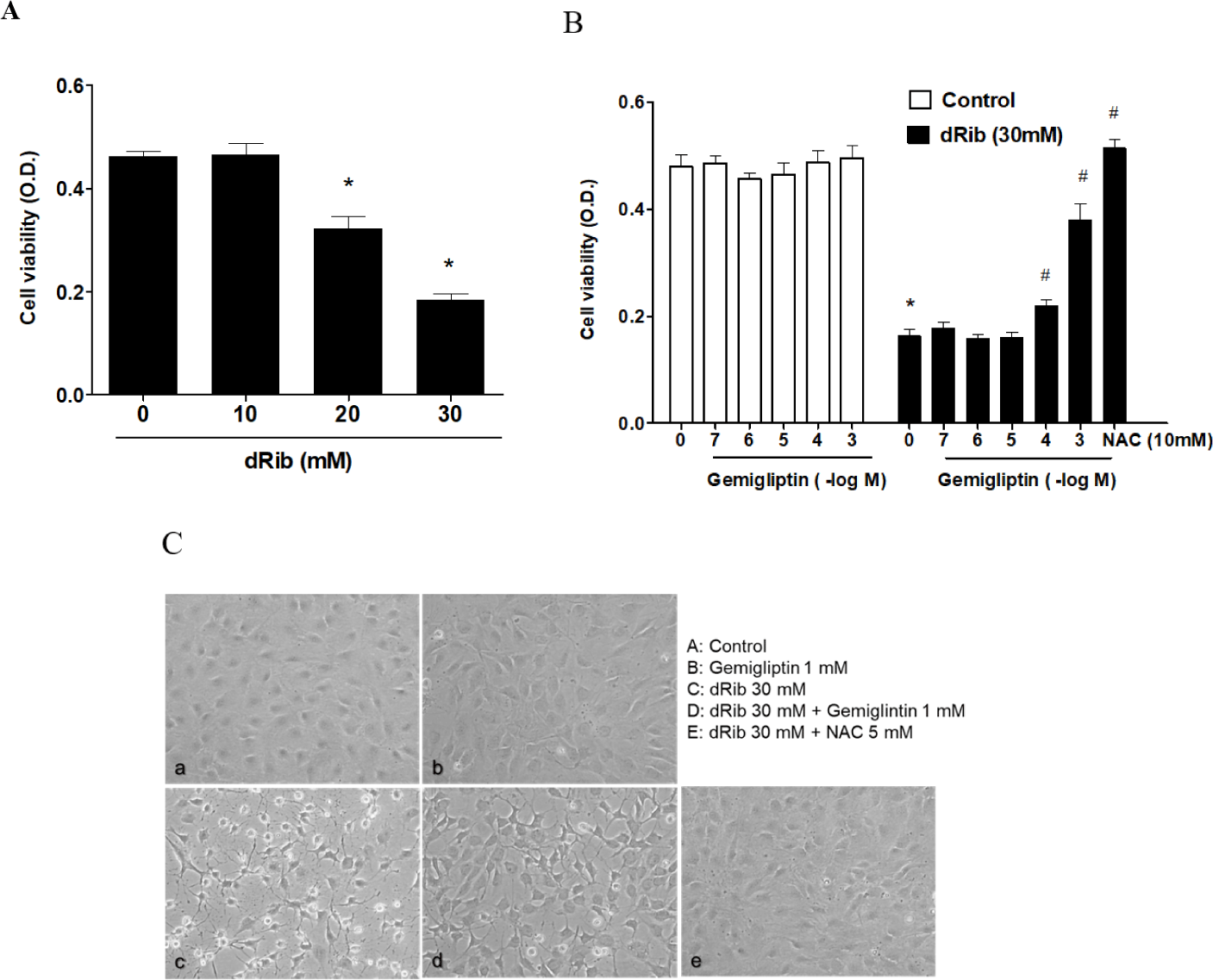
Cells were incubated in α-MEM containing 0.5% FBS to evaluate the osteoblastic cell survival by gemigliptin. We treated the cells with various concentrations (10-7–10-3 M) of gemigliptin for 24 h and then determined cell viability. Gemigliptin increased the cell viability under dRib-mediated reduction from 10-4 M concentration of gemigliptin (Fig. 1B). At 10-3 M, gemigliptin dramatically enhanced cell viability. The antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) was used as a positive control for dRib-induced cell damage. 10 mM NAC treatment completely reversed the effects of dRib on cell viability. This positive control for MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells was adopted from our previous study [14]. Morphological changes in the dRib-treated group were compared with controls and the dRib + gemigliptin treatment group. The control cells were flat and polygonal. After exposure to dRib for 24 h, the cells were degenerated and spindle-shaped in appearance. Gemigliptin improved the morphological changes of osteoblastic cells by dRib treatment (Fig. 1C).
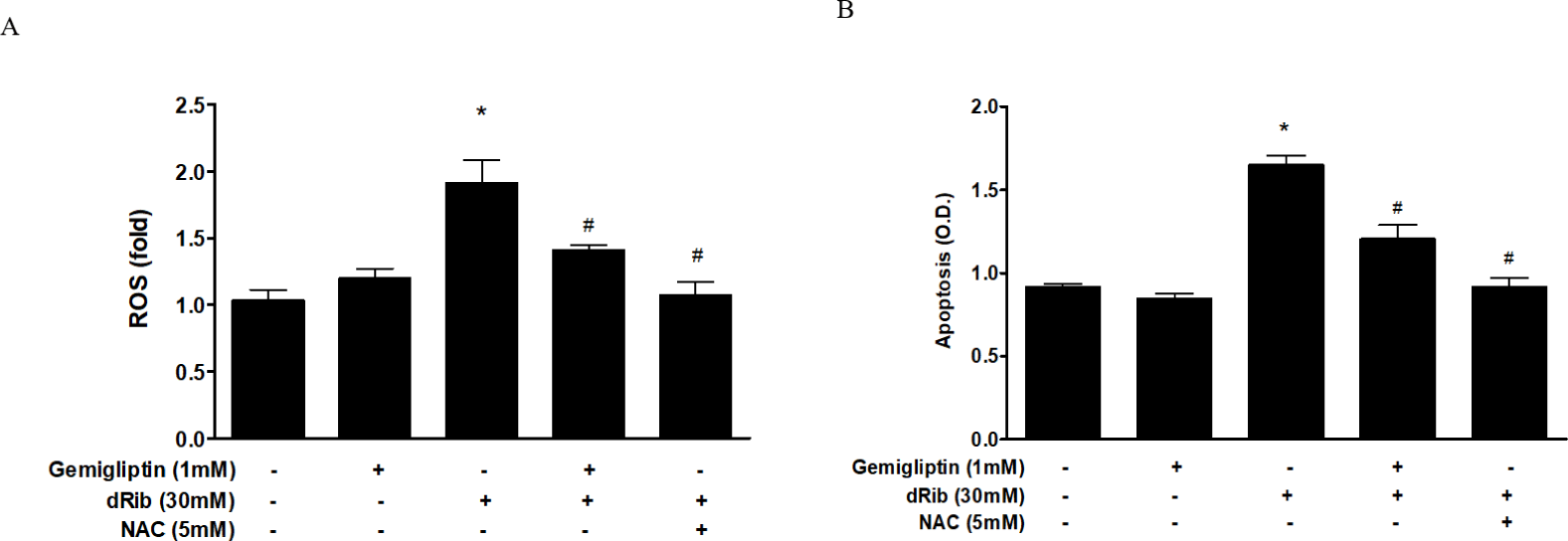
We evaluated oxidative stress by measuring ROS generation and apoptosis. By treatment of 30mM dRib, ROS generation and apoptosis approximately doubled. When 1 mM gemigliptin was given in the presence of dRib, the dRib-induced ROS generation and apoptosis was attenuated (Fig. 2). NAC reversed the dRib-induced cellular effects. The protective effect of gemigliptin on oxidative stress was not as potent as that of NAC. Gemigliptin can function as an antioxidant, thereby protecting against injury.
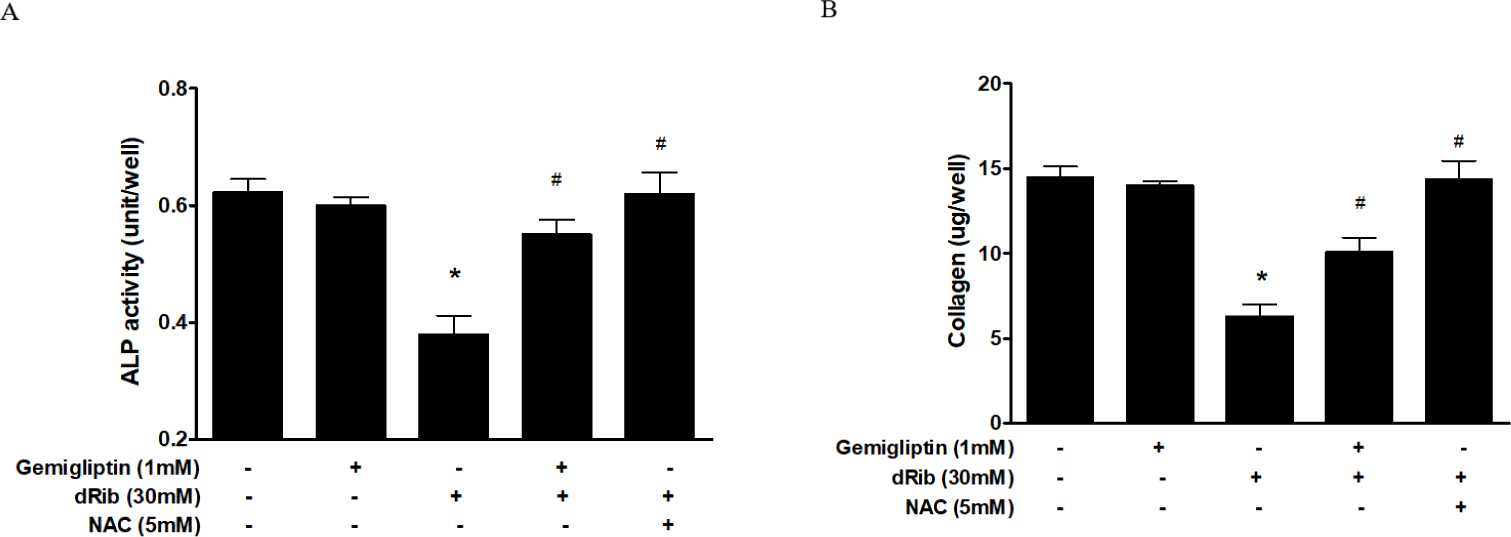
Bone ALP serves as an osteoblast phenotypic marker [15]. Increased ALP activity has been observed in differentiating osteoblasts in vitro. Osteoblastic cells produce type I collagen, an early marker of osteoblast differentiation [16]. In this study, we measured bone ALP and collagen as surrogate markers of osteoblast differentiation. ALP activity and collagen were significantly increased after gemigliptin treatment. When cells were treated with 1 mM gemigliptin in the presence of 30 mM dRib, ALP activity and collagen content significantly restored (Fig. 3).
We measured the mRNA levels of ALP, collagen and molecular markers of osteoblastic differentiation. Gemigliptin significantly increased the levels of ALP, collagen, osteocalcin, BMP2, BMP7 and OPN. There were no statistically significant changes in osteoblastic differentiation markers with and without the presence of 30 mM dRib (Fig. 4A).
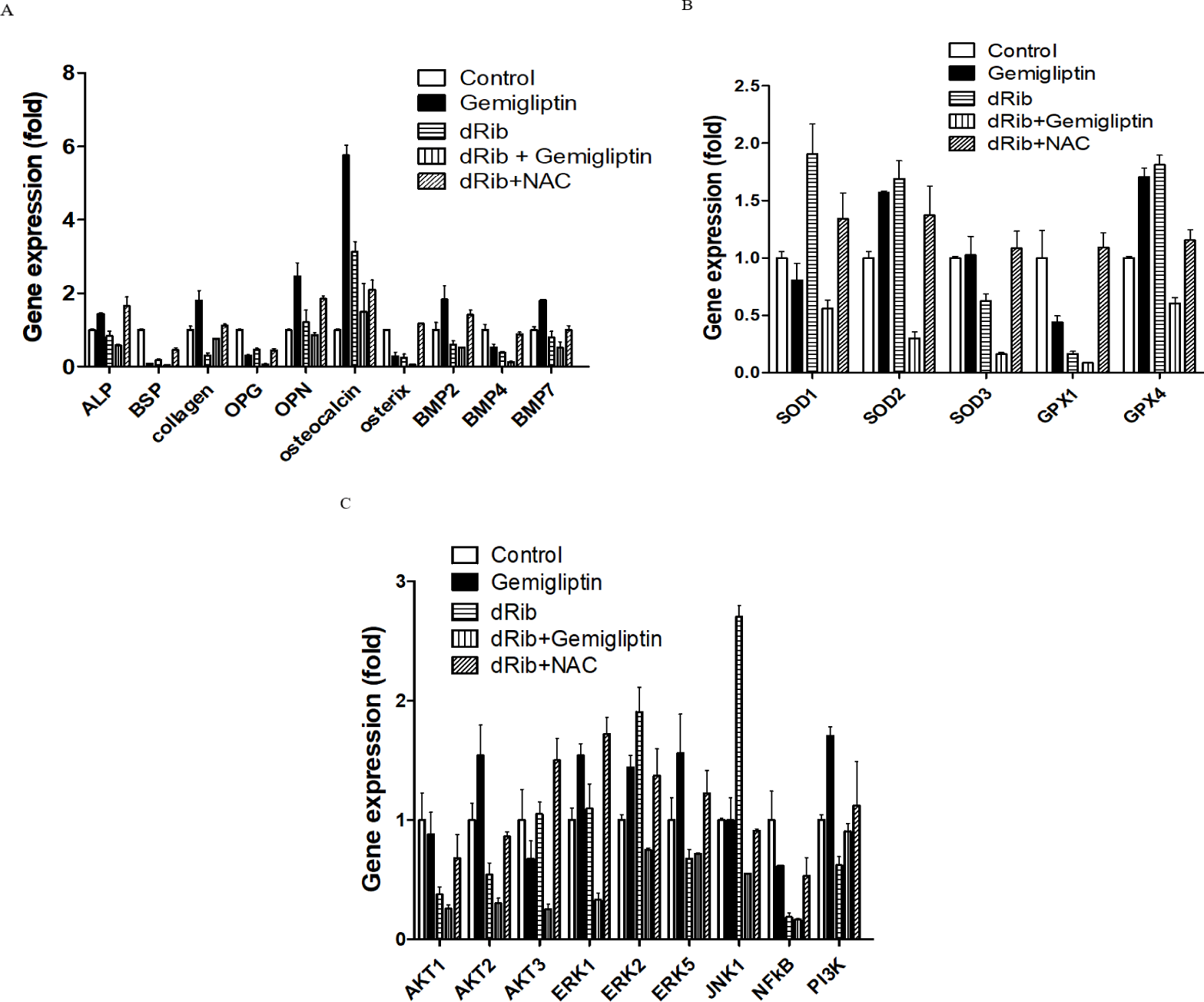
SODs catalyze dismutation of the superoxide anion into hydrogen peroxide and molecular oxygen. GPXs catalyze the reduction of hydroperoxides and glutathione to protect the cell from oxidative damage. SODs and GPXs are thus important antioxidant enzymes. We measured the changes in SODs and GPXs levels following treatment with gemigliptin with and without dRib condition. There were no significant changes in SOD1 or GPX1 expression after treatment with gemigliptin (Fig. 4B)
We measured PI3K, AKT1, AKT2, AKT3, BMP2, BMP4 and BMP7 mRNA expression levels to evaluate the effects of gemigliptin on PI3K/AKT/BMP-related osteoblastic differentiation [17]. PI3K, AKT2, BMP2 and BMP7 expression levels were increased by gemigliptin treatment. The expression levels of ERK1, ERK2 and ERK5 were also increased by gemigliptin treatment. Under dRib condition, gemigliptin increased the expression level of PI3K (Fig. 4C).
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the effects of gemigliptin on dRib-induced oxidative damage in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cell cultures. Diabetes-associated bone disease may involve the production of poor quality bone. Previous studies have demonstrated that hyperglycemia attenuates proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts to induce poor bone quality [18]. dRib-induced cellular dysfunction and apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cells was well characterized in our previous studies [13, 14]. Here we found that gemigliptin had a profound effect on osteoblastic differentiation.
We observed a dose-dependent decrease in cell viability caused by dRib (Fig. 1A). Based on this result, we used a dose of 30 mM dRib in subsequent biochemical assays. CCK-8 assays showed that 10-7–10-3 mM gemigliptin partially reversed the dRib-mediated reduction in cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. Gemigliptin improved the morphological changes in osteoblastic cells induced by dRib. We measured ROS generation and apoptosis to evaluate oxidative stress caused by dRib in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. When the cells were treated with dRib, ROS generation and apoptosis increased, while treatment with gemigliptin in the presence of dRib attenuated all dRib-induced effects. The antioxidant NAC reversed dRib-induced cellular oxidative stress (Fig. 2). These findings indicate that gemigliptin can function as an antioxidant, protecting osteoblasts from oxidative stress. Treatment with gemigliptin increased ALP activity and collagen contents. However, gemigliptin did not increase ALP or other bone-related markers in the presence of dRib. Bone ALP is a glycoprotein localized in the plasma membrane of osteoblasts and a marker of the osteoblastic phenotype [15]. High levels of ALP activity indicate that both pre-osteoblasts and osteoblasts are actively differentiating.
We further investigated gemigliptin’s effects on osteoblast differentiation in the gene expression levels. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is associated with BMP activation [19]. BMPs are the most potent regulators of osteoblast differentiation. BMPs stimulate ALP activity, collagen synthesis, parathyroid hormone responsiveness and Osteocalcin (OC) production in osteoblasts [20, 21]. Osteocalcin is a pro-osteoblastic bone-building, bone mineralization and calcium ion homeostasis marker in osteoblastic differentiation [22]. The PI3K/AKT/BMP axis is thought to be a key regulator in the differentiation of osteoblasts. Our results showed that gemigliptin may stimulate this axis by increasing PI3K, AKT, BMP2, BMP7, ALP and OC gene expression. The expression level of PI3K was increased by gemigliptin treatment under dRib condition. Improved bone quality by gemigliptin may be associated with PI3K/AKT/BMP axis. Another potential pathway that gemigliptin acts through is ERK/MAPK/osteoblast differentiation [23]. This axis also induces matrix mineralization [24]. Gemigliptin increased ERK1, ERK2 and EKR5 gene expression in our study. The ERK signal induces an increase in BMP2-dependent osteoblast differentiation, which is consistent with our results.
We investigated the potential of gemigliptin in improving bone quality during the treatment of patients with diabetes, but there are some limitations. First, gemigliptin did not increase osteoblastic marker expression in the presence of dRib. It would be more suitable to investigate the effects of gemigliptin under low oxidative conditions rather than in the presence of dRib in future studies since dRib is the strongest reducing sugar [25]. The difference of ALP-related markers after gemigliptin treatment is needed to elucidate the exact mechanism. Secondly, mechanistic study did not investigate protein levels and under hyperglycemic condition. Hyperglycemic condition in vivo study is needed in the future study. Third, the long-term effects of gemigliptin exposure on bone mineral density in a diabetic animal model should be investigated. Fourth, we used the MC3T3-E1 cell line and did experiments in vitro. To elucidate the effect of gemigliptin’s effect on bone mineralization, further study is needed in primary osteoblast culture setting using bone marrow. This scope is future study theme to elucidate the physiological pathway of gemigliptin in bone mineralization.







