List of Articles
Life Cycle. Vol. 2, 2022
State-of-the-Art Reviews

Effect of physical activity on COVID-19 and underlying mechanisms
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e20
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e20
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e20
ABSTRACT
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has been rapidly transmitted globally since December 2019. As COVID-19 was caused by a novel coronavirus, people only counted on their innate immune system in the early COVID-19 pandemic. However, given that the defense against viral infec...
Effect of COVID-19 pandemic on diagnosis and treatment pattern of prostate cancer: a comprehensive literature review, phase 1
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e19
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e19
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e19
ABSTRACT
Since its outbreak in late 2019, the COVID-19 pandemic has brought many changes to medical practice, including the care and management methods regarding prostate cancer. Patients with prostate cancer are exposed to high risk of infection, hospitalization, and death due to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), while other... 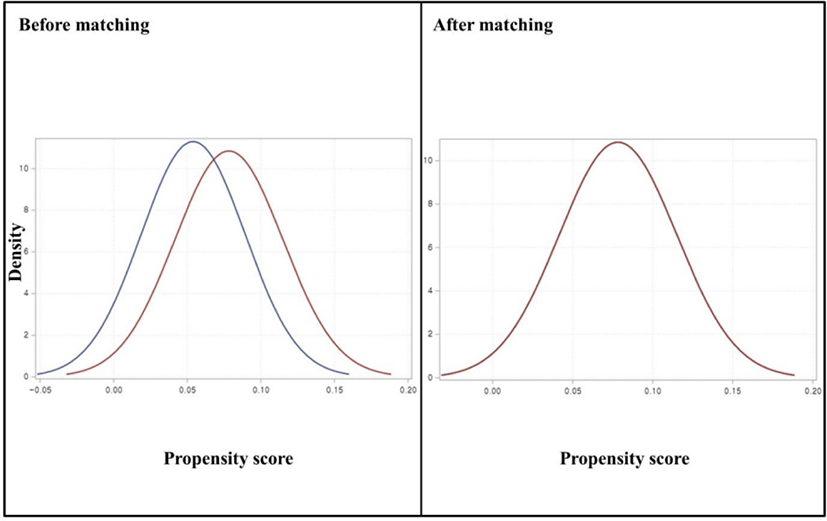
Propensity score matching for causal inference and reducing the confounding effects: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e18
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e18
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e18
ABSTRACT
Since the development of research methodology, there has always been keen interest in developing the accuracy of the research by comparing covariates. Propensity score is useful when the research covers many variables which are not intended to be included as independent variables, thus allowing the removal of certain covariates from the model. This... 
Demographic, transmission, and clinical characteristics associated with human monkeypox infection, October 2022: a systematic analysis for World Health Organization database and brief review
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e17
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e17
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e17
ABSTRACT
The monkeypox (MPX) is an unusual viral disease which, until recently, has rarely been detected outside of Africa. A total of 71,237 confirmed cases of MPX, as of October 6th, 2022, had been discovered in 109 countries in the matter of months. The risk factors of MPX are men who have sex with the same gender (prevalence 90.0%, 95% CI, 89.5 to 90.4)... 
Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality of human monkeypox infection in 107 countries and territories, October 2022: a systematic analysis for World Health Organization database and rapid review
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e16
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e16
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e16
ABSTRACT
The monkeypox is an unusual viral disease which, until recently, has rarely been detected outside of Africa. Approximately over 70,000 laboratory-verified or suspected cases of human monkeypox have been discovered in at least 107 countries in a matter of months. A total of 71,237 laboratory confirmed cases, 1,097 probable cases, and 26 related deat...
Original Research Article

Global, regional, and national COVID-19 vaccination rate in 237 countries and territories, March 2022: a systematic analysis for World Health Organization COVID-19 Dashboard, Release 2
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e15
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e15
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e15
ABSTRACT
Objective: We aimed to better understand the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic through analysis of disruptions in a global, regional, and national status of COVID-19 vaccination coverage compared by a global scale, World Health Organization regions, World Bank income groups, and each country. Methods: Global datasets of 237 countries and territories ... 
Global, regional, and national disruptions to COVID-19 vaccine coverage in 237 countries and territories, March 2022: a systematic analysis for World Health Organization COVID-19 Dashboard, Release 1
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e14
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e14
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e14
ABSTRACT
Objective: Measuring coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination is crucial in improving global public health system during the pandemic. However, there is limited supporting data needed in order to identify the global, regional, and national status of the COVID-19 vaccination coverage. Given to such limitations, this study aimed at investigati...
State-of-the-Art Reviews

The importance of a World Health Organization international pharmacovigilance database (VigiBase): novel methods for safety monitoring and surveillance of medical products
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e13
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e13
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e13
ABSTRACT
Pharmacovigilance and medical product safety issues are important for all global citizens. Previous studies have analyzed the disaster caused by thalidomide in 1961. In 1963, the 16th World Health Assembly was determined to create the World Health Organization (WHO) Pilot Research Project for International Drug Monitoring in order to develop and un... 
The effects of systemic corticosteroid on pediatric community-acquired pneumonia: comprehensive review
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e12
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e12
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e12
ABSTRACT
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a highly prevalent disorder in children. The treatment options available for children with CAP are inhalation therapy and initiation of appropriate antibiotic therapy. Occasionally, CAP may progress to severe pneumonia despite appropriate therapy. While there are a few studies reporting the beneficial effects o... 
Situation reports and impacts on public health during the war in Ukraine, 24 February to 21 June 2022: World Health Organization Emergency Reports
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e11
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e11
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e11
ABSTRACT
Due to the Russian illegal invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, evident and dramatic increases were found in the numbers of war-affected populations, the refugees, individuals relocated in Ukraine, and civilian injuries and deaths as the war is escalated. The war has delivered great pressures and demands for the Ukrainian health division. Food...
Original Research Article
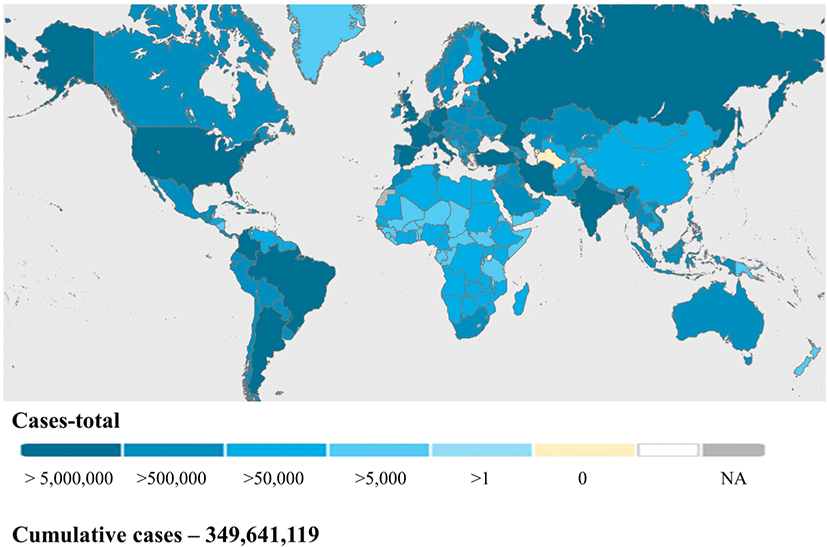
Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality of COVID-19 in 237 countries and territories, January 2022: a systematic analysis for World Health Organization COVID-19 Dashboard
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e10
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e10
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e10
ABSTRACT
Objective: To estimate global, regional, and national incidences and mortality of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in 237 countries and territories since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic to 31 January, 2022. Methods: Comprehensive estimates were produced through global, regional, and national studies of cumulative severe acute respirato...
State-of-the-Art Review
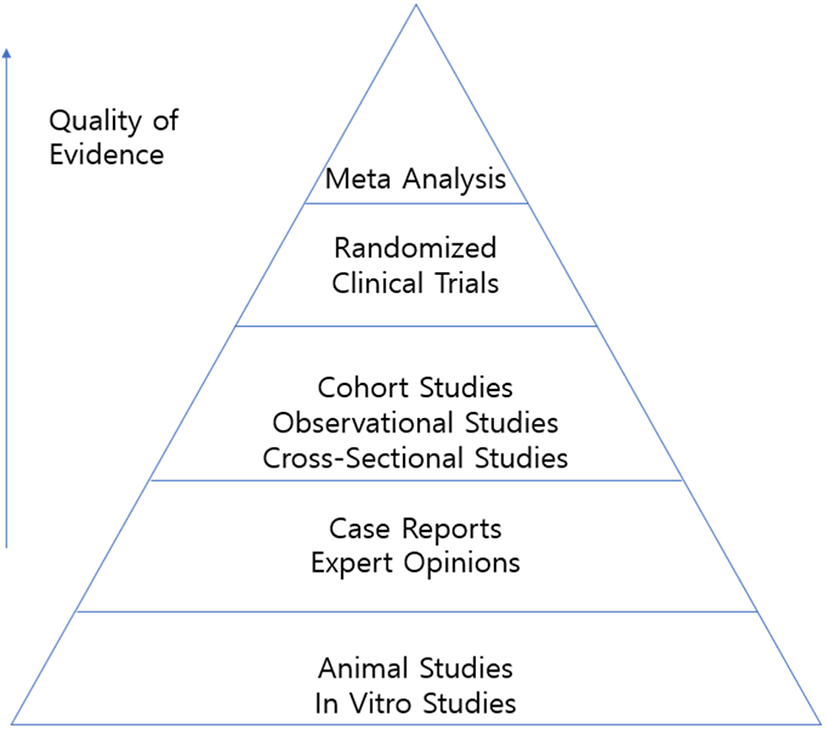
PRISMA 2020 statement and guidelines for systematic review and meta-analysis articles, and their underlying mathematics: Life Cycle Committee Recommendations
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e9
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e9
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e9
ABSTRACT
The paper discussed the overall aspects of systematic review and meta-analysis and explored the main mathematical context of meta-analysis. This included various methods of analyzing the effect size and obtaining the average effect size depending on the variable type. In doing so, methods of obtaining effect sizes in continuous outcome variables, c... 
Global Burden of Disease study at the World Health Organization: research methods for the most comprehensive global study of disease and underlying health policies
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e8
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e8
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e8
ABSTRACT
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) is a compass that navigates researchers and clinicians in discovering the latest knowledge and the current status of health for populations and countries worldwide. The GBD helps to present various methods in evaluating health-related quality of life and assess the health burden, economic burden, years of life los... 
How serious is the Omicron variant? transmissibility, genomics, and responses to COVID-19 vaccines, and ‘Stealth’ Omicron variants
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e7
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e7
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e7
ABSTRACT
Since its emergence on November 9, 2021, the Omicron variant has spread quickly across the globe as a new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and became the variant of concern at an astonishingly rapid rate. This new variant was found to be a massively mutated virus from the original virus formation. The World Health Organi... 
Extrapulmonary clinical manifestations of COVID-19: an umbrella review of meta-analysis
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e6
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e6
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e6
ABSTRACT
Since its emergence, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), compared to other coronavirus diseases throughout history, has generated large waves of infection with symptoms such as fever, chills, cough, fatigue, headache, and sore throat appeared. Despite many efforts and gains through meta-analyses of the symptoms of COVID-19 thus far, there has ... 
Vaccine strategy against COVID-19 with a focus on the Omicron and stealth Omicron variants: Life Cycle Committee Recommendations
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e5
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e5
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e5
ABSTRACT
The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), was first discovered in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, and was consequently transmitted across the world. Further, within a year of its initial discovery, vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 were developed using diverse t... 
COVID-19 vaccines and coronavirus 19 variants including alpha, delta, and omicron: present status and future directions
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e4
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e4
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e4
ABSTRACT
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by a coronavirus, also called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It has caused urgent global health problems worldwide. The rapid spread of this pathogen, the development of its variants, and the escalating number of patients and their deaths prompted scientists to take up the... 
Regression analysis for continuous independent variables in medical research: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e3
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e3
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e3
ABSTRACT
Variables measured in medicine are usually continuous, such as blood pressure, serum glucose, and drug dosage. There are statistical methods to confirm whether these variables act as independent variables that cause an outcome. Most of these methods are types of regression analysis. In this article, starting with a simple correlation coefficient, l...
Original Research Article
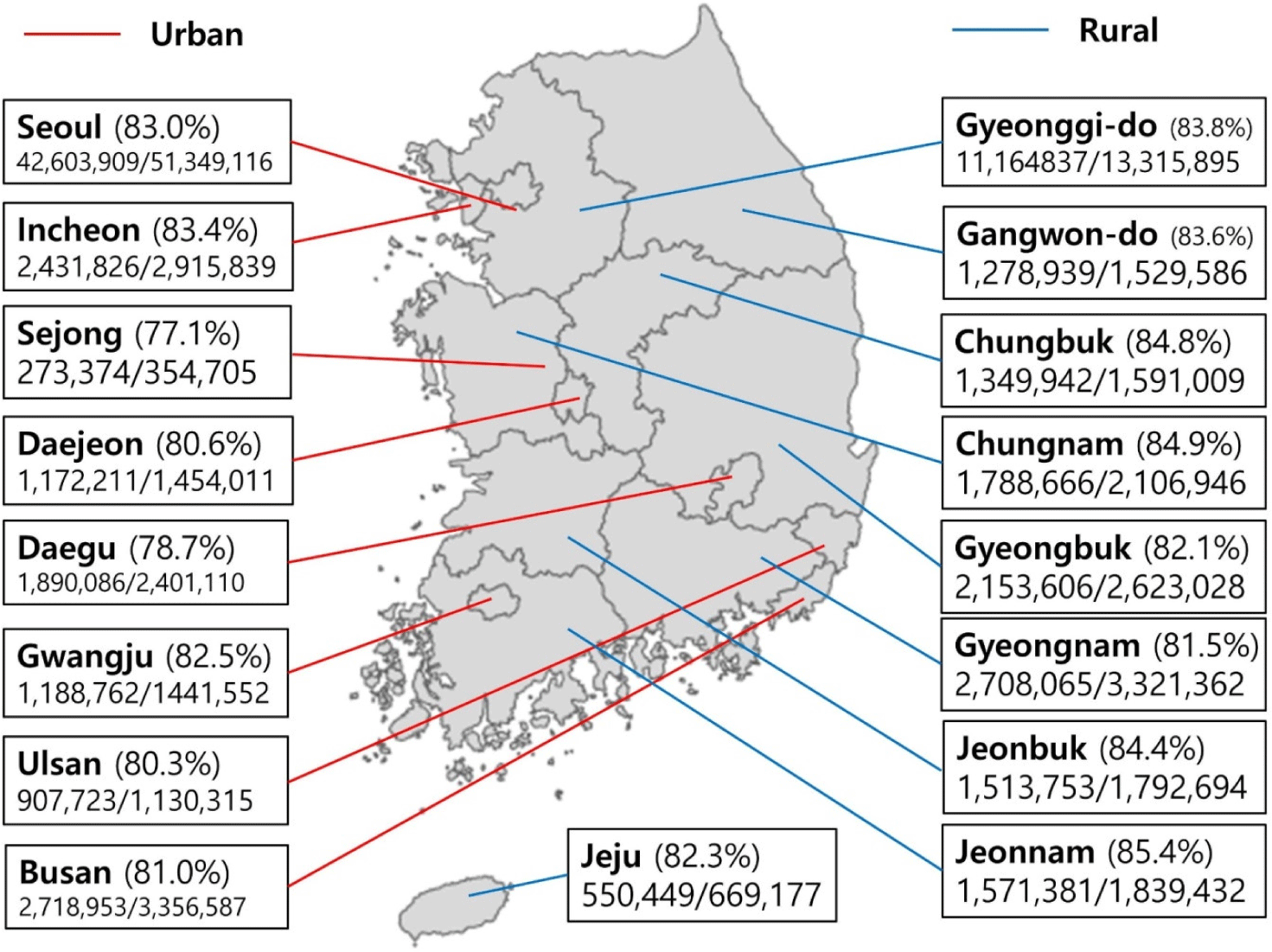
Nationwide COVID-19 vaccination coverage and COVID-19 incidence in South Korea, January 2022: a national official report
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e2
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e2
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e2
ABSTRACT
Objective: To reduce the risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) illness, and COVID-19 related death, all persons in South Korea should stay up to data with recommended COVID-19 vaccinations. This study investigated the rates and effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccina...
State-of-the-Art Review
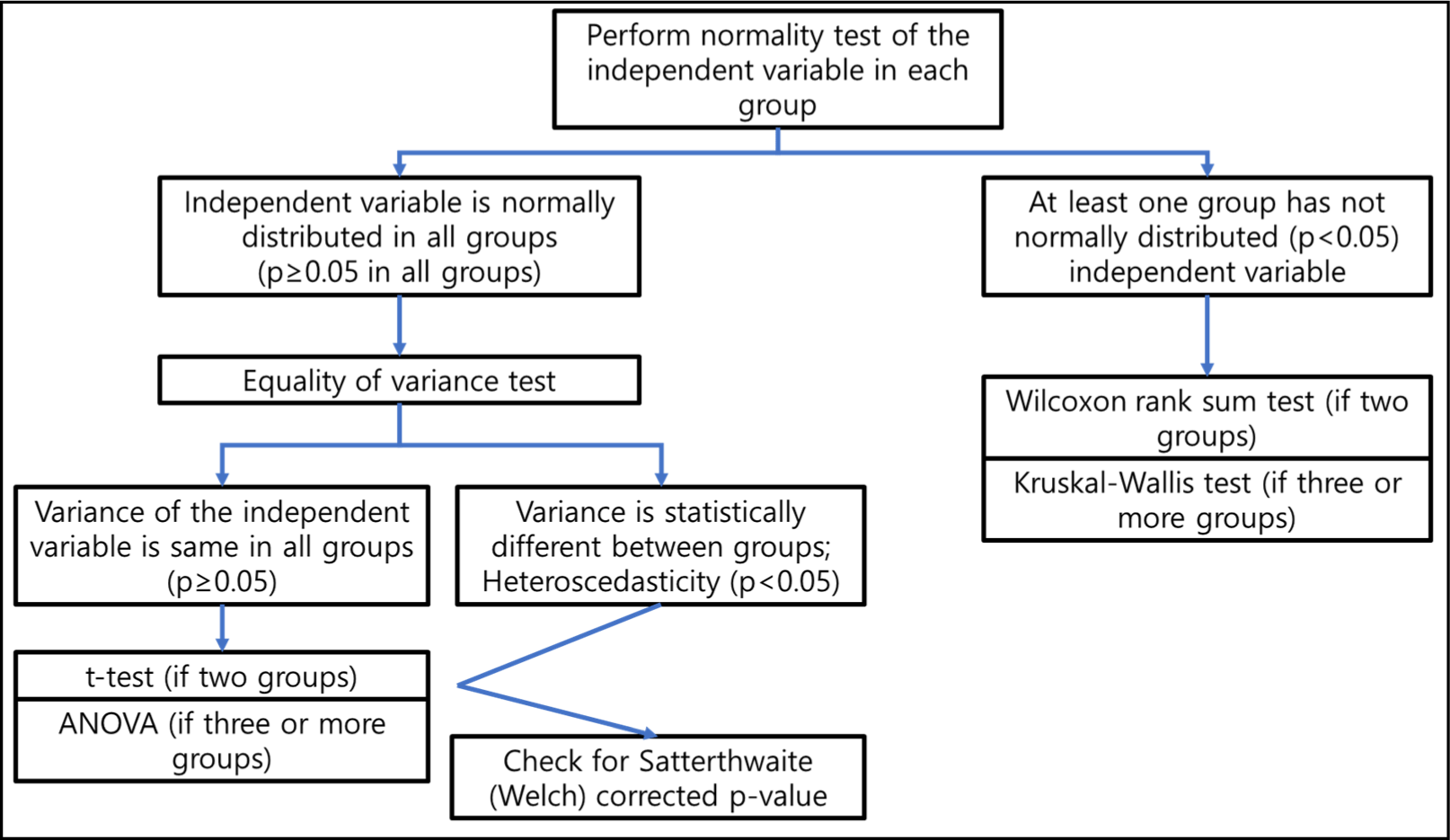
Methods for testing statistical differences between groups in medical research: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2022;2:e1
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e1
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e1
ABSTRACT
In medical research, when independent variables are categorical (i.e., dividing groups), statistical analysis is often required. This situation mostly occurs on randomized controlled trials and observational studies that have multiple patient groups. Also, when analyzing continuous independent variables in a single patient group, breakpoints can be... 







