List of Articles
Life Cycle. Vol. 4, 2024
Original Research Article
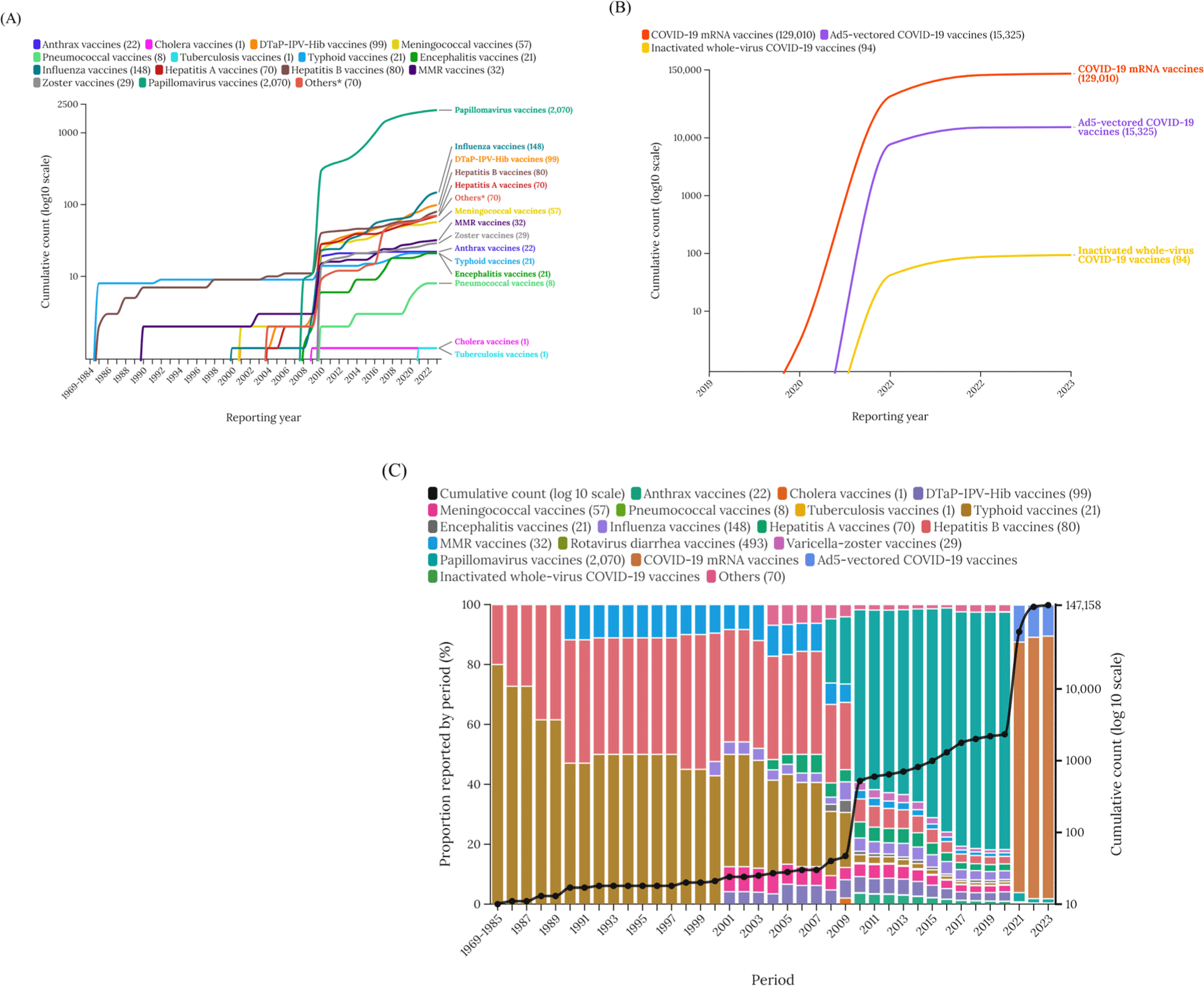
Regional burden of vaccine-associated menstrual disorders and sexual dysfunction: a retrospective study
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e12
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e12
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e12
ABSTRACT
Objective: While previous studies have shown that vaccine-induced adverse events differ between sexes, there is still a gap in research analyzing sex-specific reproductive system disorders caused by vaccines. Thus, this study aims to address this gap by identifying the vaccines that most commonly influence the reproductive system in each sex, with ... 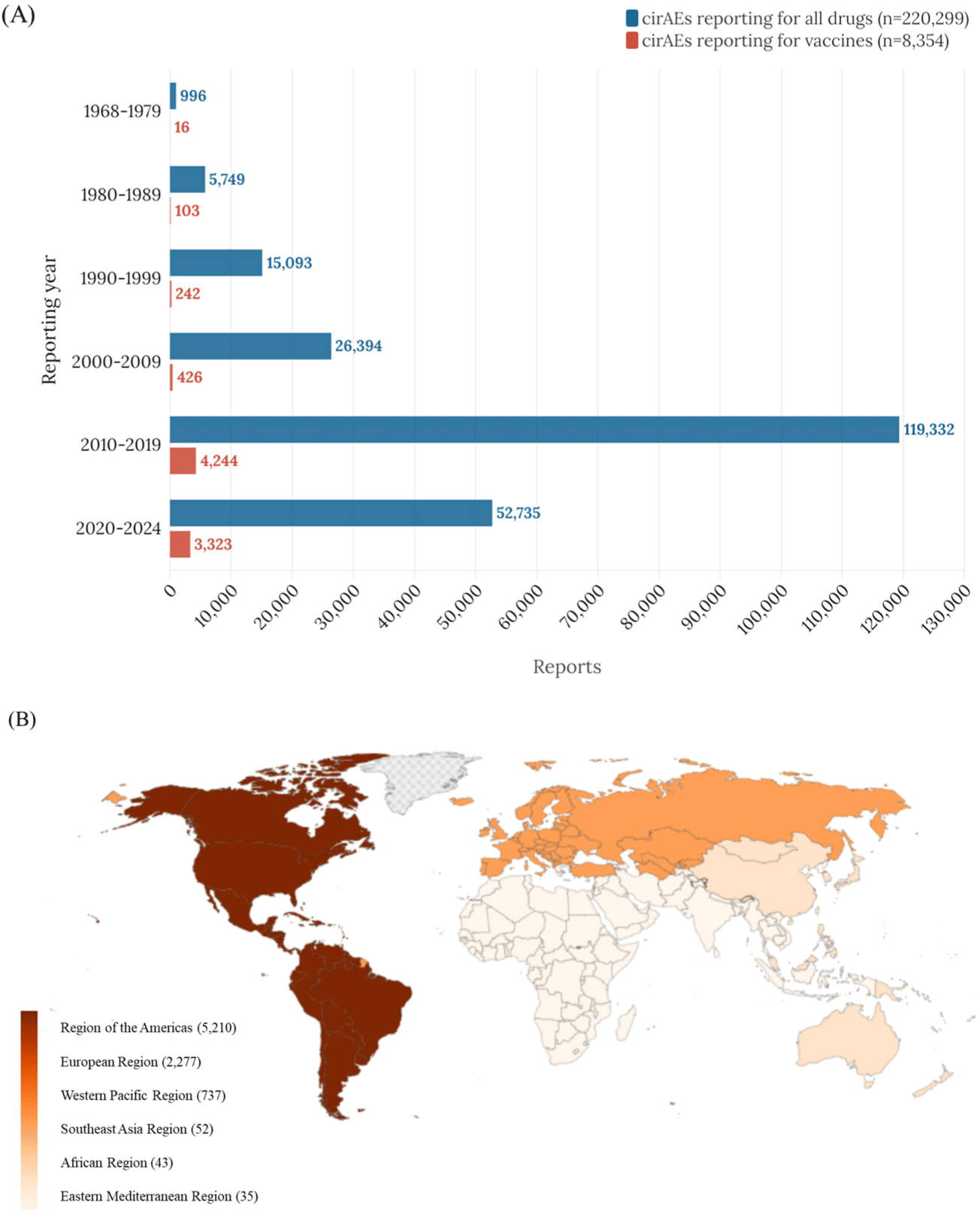
Global burden of vaccine-associated cutaneous immune-related adverse events, 1968–2024: An international pharmacovigilance study
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e11
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e11
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e11
ABSTRACT
Objective: Since vaccines stimulate the immune system, monitoring immune-related adverse events is critical. This study focuses on the global incidence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events (cirAEs), the most common type of immune-related adverse events, and their associations with different vaccine types. Methods: This study is based on the g...
State-of-the-Art Reviews
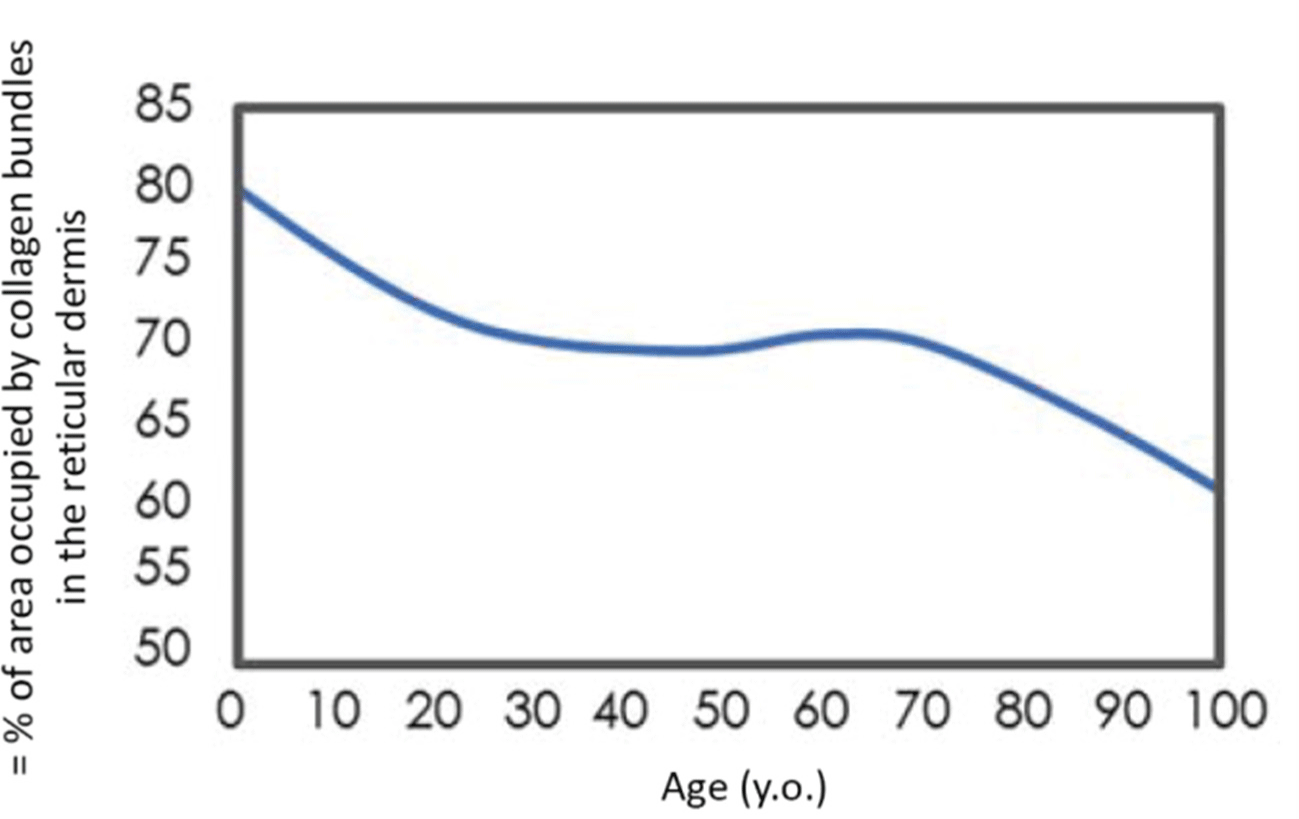
Contemporary insights into the collagen-stimulating mechanism of polylactic acid: a new paradigm in dermal fillers using poly-L-lactic acid fillers
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:10
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e10
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e10
ABSTRACT
Regardless of variances in lifestyle and environment, the initial indications of facial aging typically manifest between the ages of 20 and 30 years. Collagen loss is the most significant factor in the emergence of external signs of skin aging. Polylactic acid (PLA) is a notable stimulant of neocollagenesis and has become widely used as an injectab...
Letters

Vulvar rejuvenation and high-intensity focused ultrasound: the pioneering of an aesthetic field
Life Cycle 2024;4:e9
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e9
HTML
PDF
PubReader
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e9
Original Research Article
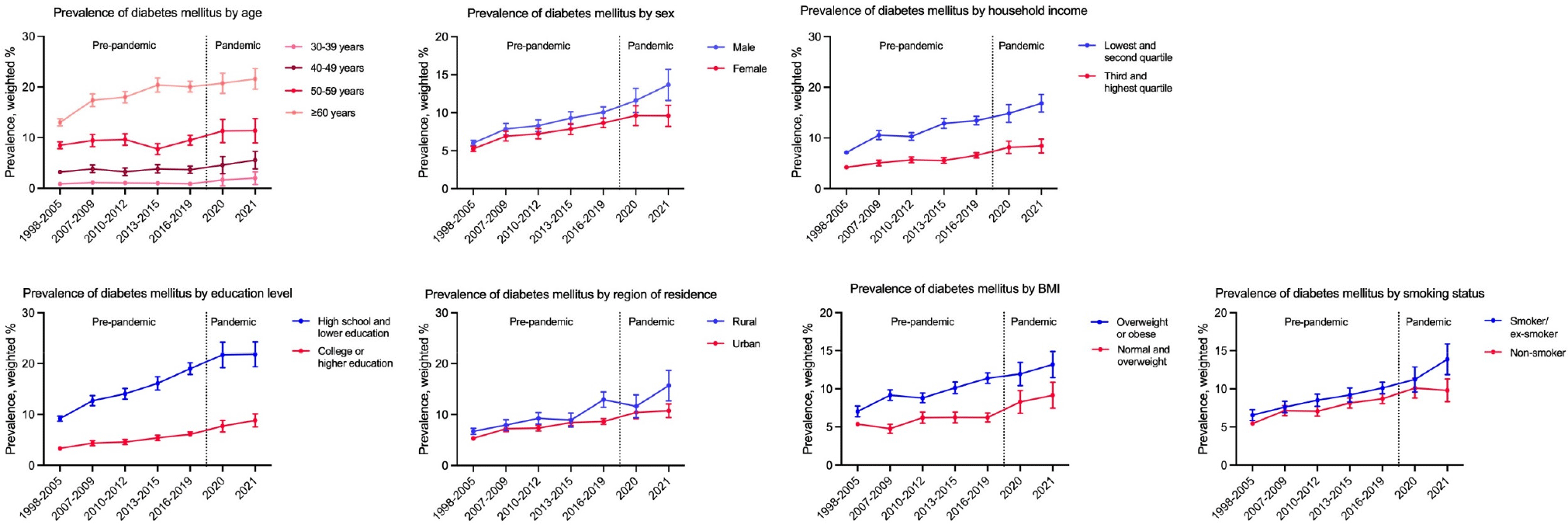
A National trends in type 2 diabetes in South Korea, including the COVID-19 pandemic, 1998-2021: A nationally representative survey study
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e7
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e7
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e7
ABSTRACT
Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with worse outcomes for people with diabetes, including increased mortality, while the long-term impact of the pandemic on diabetes prevalence is still underestimated. Thus, we aimed to analyze long-term prevalence trends of type 2 diabetes in South Korea from 1998 to 2021, encompassing the befor... 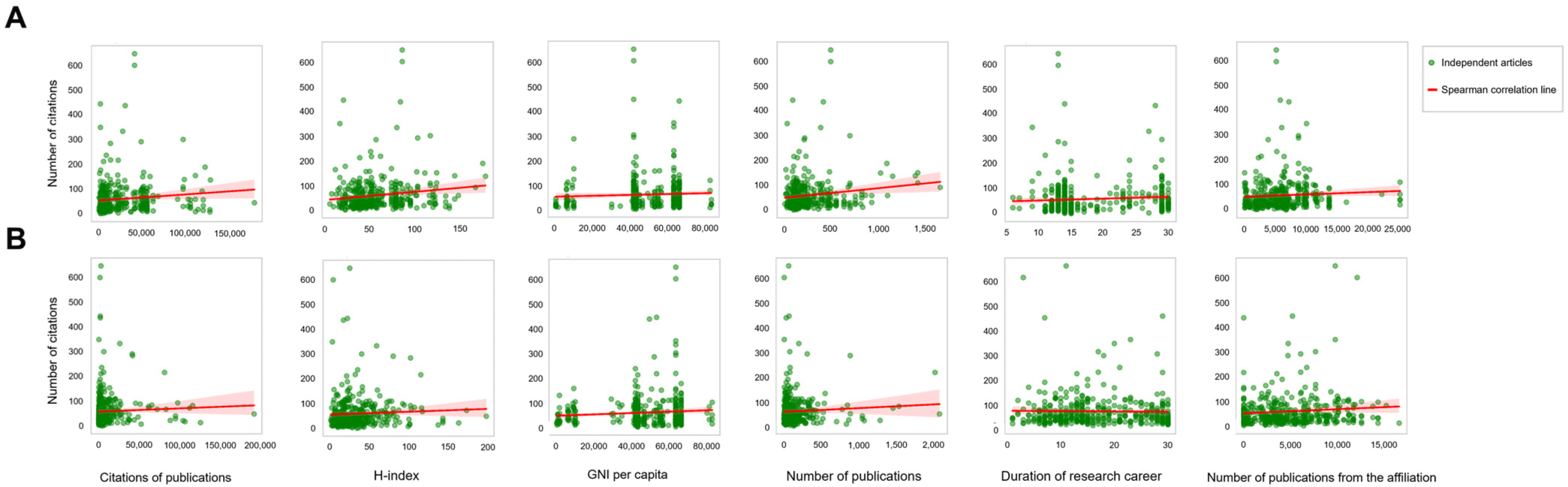
Are citation counts of articles related to outcomes and legacies of authors and journal editors? (CAROL): a cohort study
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e8
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e8
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e8
ABSTRACT
Objective: To investigate the association between the number of citations each article received and quantitative factors of journal editors or corresponding authors. Methods: We performed retrospective cohort study using corresponding author and editor information of articles published in PLOS Medicine. The number of citations for each article and ... 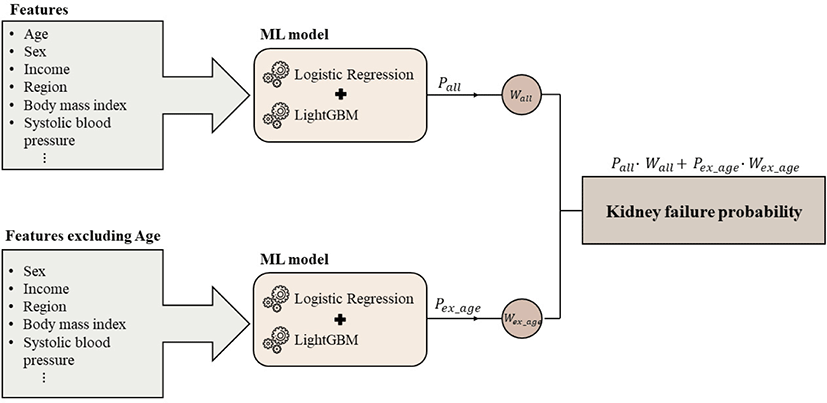
Machine-learning prediction of kidney failure occurrence based on regular health check-up data: a nationwide cohort dataset in South Korea
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e6
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e6
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e6
ABSTRACT
Objective: While prior research developed numerous machine learning (ML) models for disease prediction and demonstrated their potential, there has yet to be research on models concerning the prediction of kidney failure and its associated risk factors using simple, regular health check-up data. Thus, this study aimed to develop a ML model capable o... 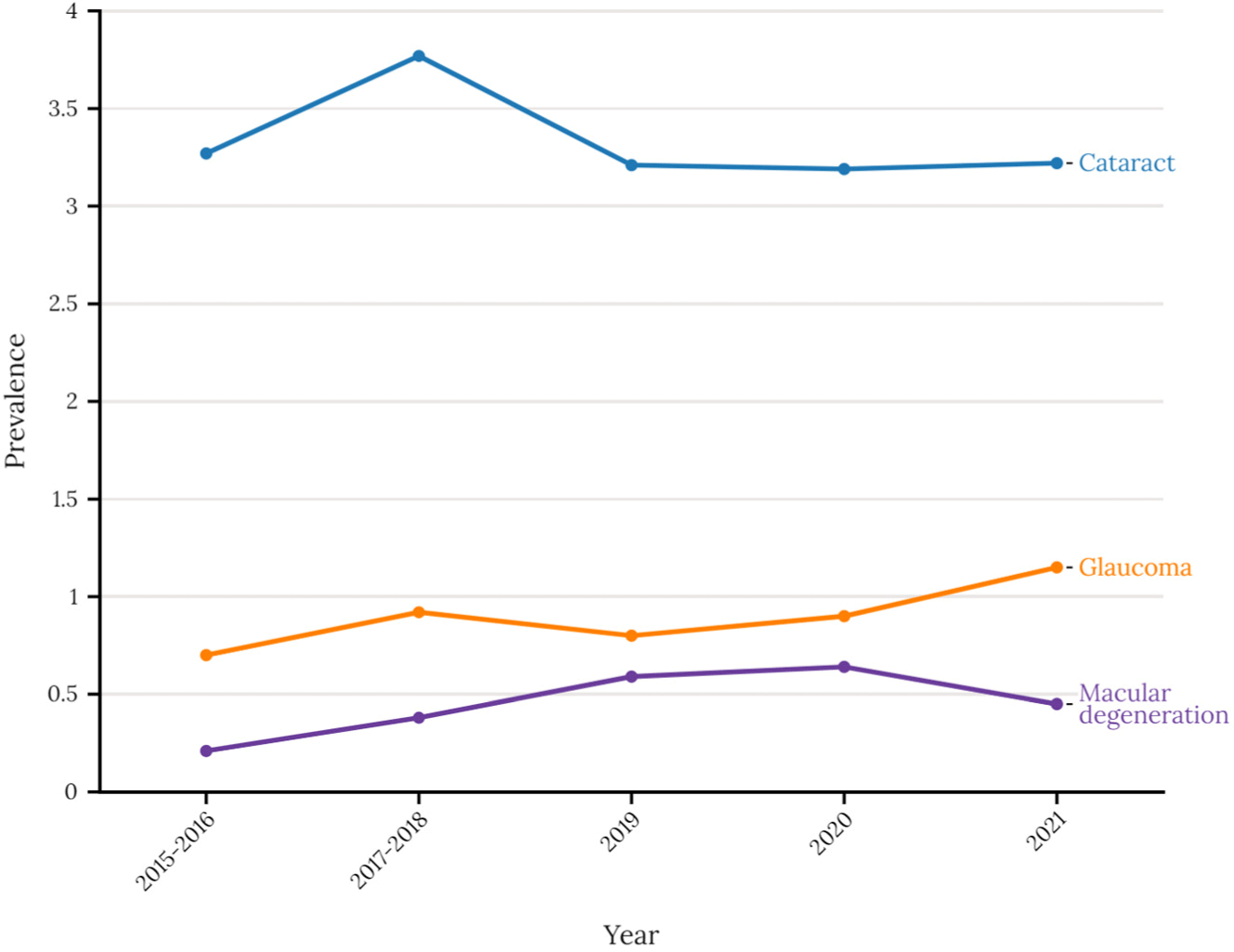
Nationwide trends in the prevalence of cataract, glaucoma, and macular degeneration among Korean adults amid the COVID-19 pandemic, 2015-2021: A representative study in South Korea
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e5
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e5
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e5
ABSTRACT
Objective: Understanding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the prevalence of key ocular diseases—cataracts, glaucoma, and macular degeneration—in the general population remains a critical yet understudied area. This study aimed to assess the long-term national prevalence of cataract, glaucoma, and macular degeneration in South Korea, consi... 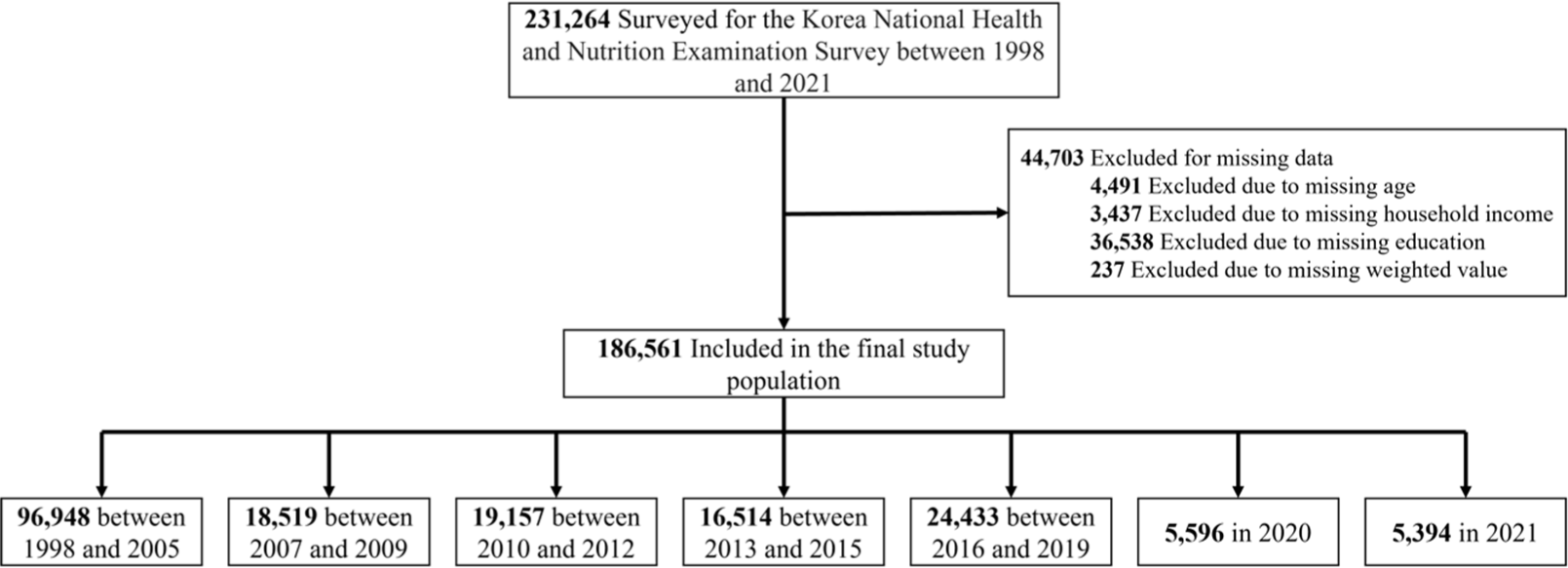
National trends in the prevalence of tuberculosis before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, 1998-2021: a nationwide representative study in South Korea
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e4
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e4
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e4
ABSTRACT
Objective: In this study, we investigate changes in the prevalence of tuberculosis (TB) before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea, analyzing the effects of age, socioeconomic, and environmental variables on TB trends over a period of 24 years. Investigation into the association between TB and the COVID-19 pandemic can accelerate advanc...
State-of-the-Art Reviews
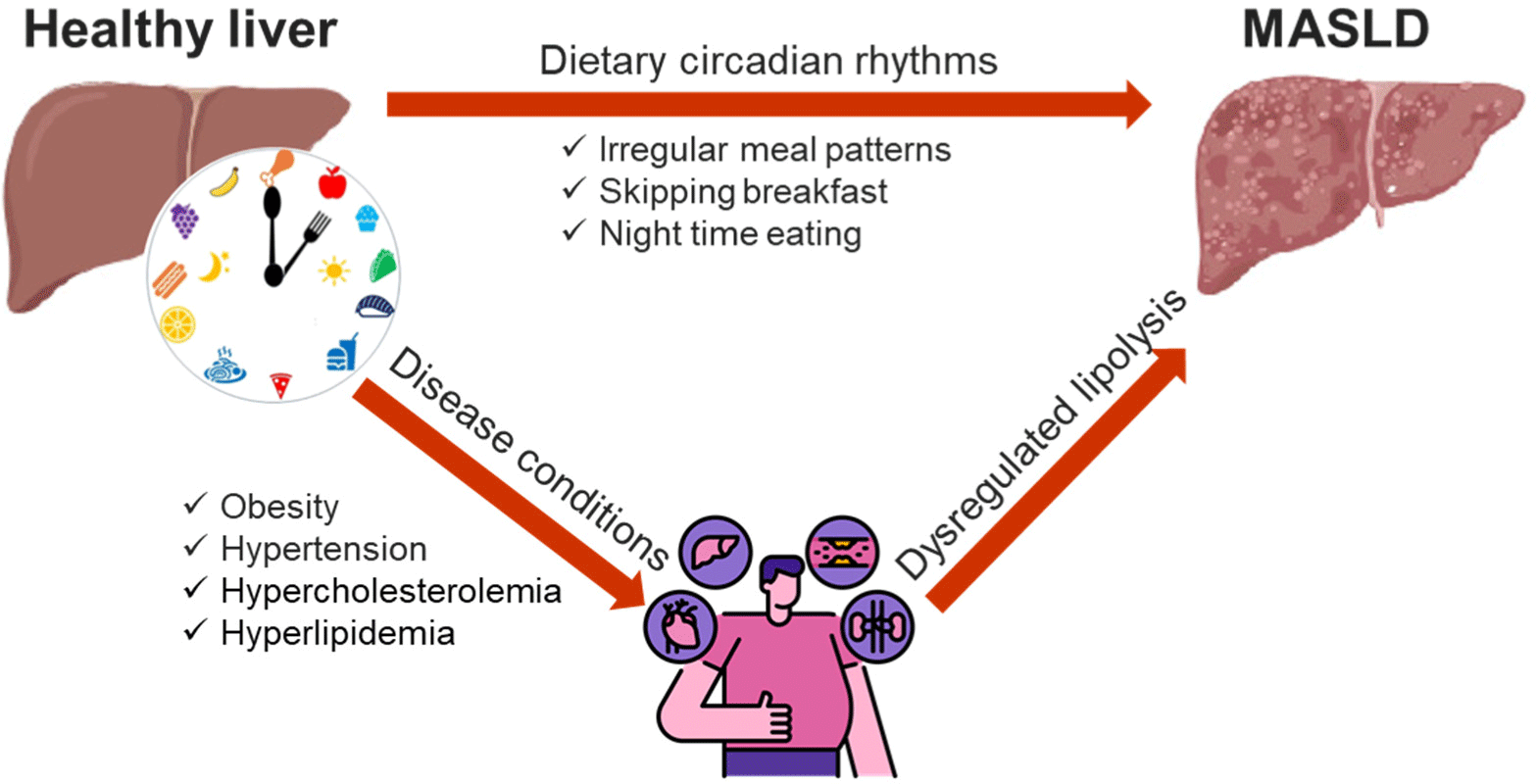
Association between dietary circadian rhythms and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease risk
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e3
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e3
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e3
ABSTRACT
Irregular or late eating patterns have been increasingly associated with a higher risk of developing metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which stands as the most prevalent hepatic disorder globally. These eating habits are believed to disrupt the body’s circadian rhythm, a critical factor involved in regulating lipid...
Letters
Association of transitioning from combustible cigarettes to noncombustible nicotine or tobacco products with subsequent cancer risk: a nationwide cohort study in South Korea
Life Cycle 2024;4:e2
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e2
HTML
PDF
PubReader
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e2
Original Research Article
Trends in prevalence of asthma and COVID-19 pandemic-related factors in South Korea: a post-hoc analysis
HTML
PDF
PubReader
Life Cycle 2024;4:e1
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e1
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2024.e1
ABSTRACT
Objective: There are only a few studies investigating the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the prevalence of asthma, especially between different age groups. Thus, we aimed to examine the trends of age-stratified asthma prevalence in South Koreans before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: This study utilized data derived from the Korea N... 







